OUR TECHNOLOGY
Recombinant multi-target immunogens based in Multiple Isomeric Epitopes targeting neurogenic inflammation.
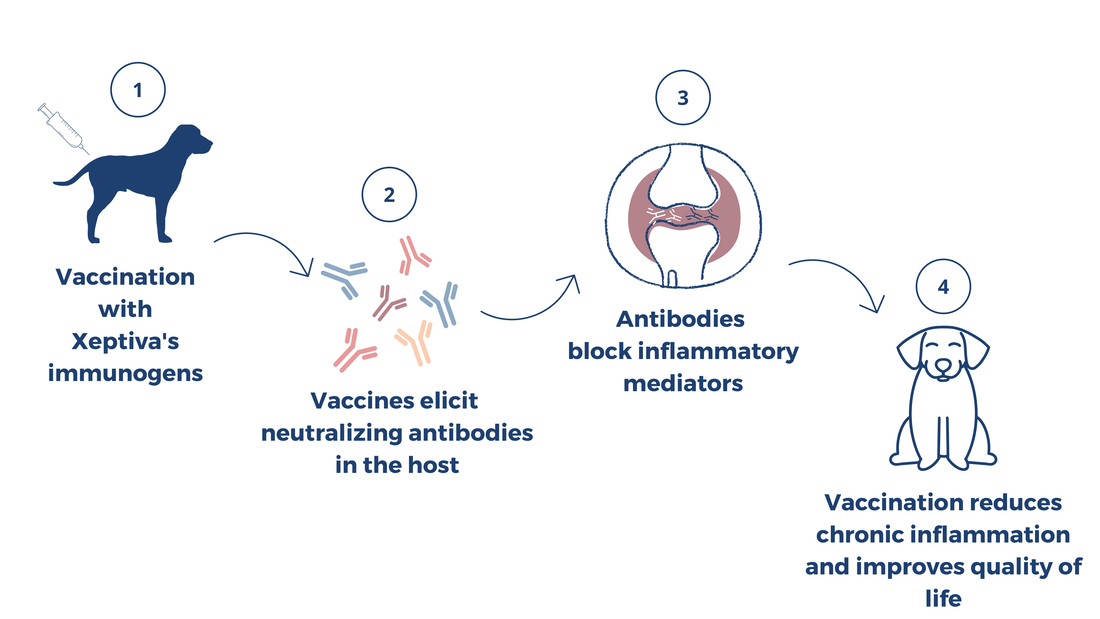
1
Xeptiva's immunogens are multi-target fusion proteins exhibiting multiple conformational isomers of a single peptidic chain.
Immunogens lack the biological activity of targeted endogenous inflammatory mediators but share specific immunogenic structural epitopes.
2
Vaccination with Xeptiva's immunogens elicit antibodies in the host that recognize the targeted endogenous mediators involved in neurogenic inflammation, incluiding growth factors, interleukins and/or neuropeptides.
3
Vaccines generate neutralizing antibodies against two or more endogenous inflammatory mediators underlying chronic inflammation, pain, itching, tissue damage, etc.
4
Vaccination reduced chronic inflammation eliciting a long-term therapeutics effect on symptoms allowing tissue regeneration, improving quality of life.
Xeptiva's immunogens are multi-target fusion proteins exhibiting multiple conformational isomers of a single peptidic chain.
Immunogens lack the biological activity of targeted endogenous inflammatory mediators but share specific immunogenic structural epitopes.
2
Vaccination with Xeptiva's immunogens elicit antibodies in the host that recognize the targeted endogenous mediators involved in neurogenic inflammation, incluiding growth factors, interleukins and/or neuropeptides.
3
Vaccines generate neutralizing antibodies against two or more endogenous inflammatory mediators underlying chronic inflammation, pain, itching, tissue damage, etc.
4
Vaccination reduced chronic inflammation eliciting a long-term therapeutics effect on symptoms allowing tissue regeneration, improving quality of life.
RELATED publications
|
September 2017
Pain in osteoarthritis
L. Arendt-Nielsen |
May 2020
Contribution of nerves within osteochondral channels to osteoarthtritis knee pain in humans and rats
K Aso, S M Shahtaheri, R Hill, D Wilson, D F McWilliams, L N Nwoscu, V Chapman, D A Walsh |
October 2009
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pain
Al Basbaum, DM Bautista, G Sherrer, D Julius |
|
October 2022
Osteoarthritis: New insight on its Pathophysiology
S. Coaccioli, P Sarzi-Puttini, P Zis, G Rinonapoli and G Varrassi |
March 2021
Neuroimmune interactions and osteoarthritis pain: focus on microphages
T Geraghty, D Winter, R Miller, R Miller, AM Malfait |
January 2012
Neuroplasticity of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers in a mouse model of a painful arthritic joint
JR Ghiraldi, KT Freeman, JM Jimenez-Andrade, KA Coughlin, MJ Kaczmarska, G Castaneda-Corral, AP Bloom, MA Kuskowski, PW Mantyh |
|
October 2010
Nociceptor sensitization in pain pathogenesis
MS Gold & GF Gebhart |
May 2021
Protective effect of sensory denervation in inflammatory arthtritis (evidence of regultarory neuroimmune pathways in the arthritic joint)
D Kane, J C Lockhart, PV Balint, C Mann, WR Ferrell, IB Mclannes |
January 2023
The multifaceted role of mast cells in joint inflammation and arthritis
A Loucks, T Maerz, K Hankenson, A Moeser & A Colbath |
|
February 2019
Substance P and Inflammatory Pain: Getting It Wrong and Right Simultaneously
E Navratilova & F Porreca |
October 2022
Neurogenic inflammation as a novel treatment target for chronic pain syndromes
MF Seidel, T Hugle, B Morlion, M Koltzenburg, V Chapman, A MaassenVanDenBrink, NE. Lane, S Perrot, W Zieglgansberger |
April 2020
Risk Factors for Canine Osteoarthritis and Its Predisposing Arthropathies:
A Systematic Review KL Anderson, H Zulch, DG O'neill, RL Meeson & LM Collins |
|
April 2019
Spontaneous dog osteoarthritis -
a One Medicine vision RL Meeson, RJ Todhunter, G Blunn, G Nuki & AA Pitsillides |
November 2011
Identification of a central role for complement in osteoarthritis
Qi Wang, AL Rozelle, CM Lepus, CR Scanzello, JJ Song, DM Larsen, JF Crish, GBebek, SY Ritter, TM Lindstrom, I HWang, HH Wong, L Punzi, A Encarnacion, M Shamloo, SB Goodman, T Wyss-Coray, SR Goldring, NK Banda, JM Thurman, R Gobezie, MK Crow, VMI Holers, DM Lee & WH Robinson |
August 2016
Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
WH Robinson, CM Lepus, Q Wang, H Raghu, R Mao, TM Lindstrom & Jeremy Sokolove |
|
May 2019
IgE-mediated mast cell activation promotes inflammation and cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis
Q Wang, CM Lepus, H Raghu, LL Reber, MM Tsai, HH Wong, E von Kaeppler, N Lingampalli, MS Bloom, N Hu, EE Elliott, F Oliviero, L Punzi, NJ Giori, SB Goodman, CR Chu, J Sokolove, Y Fukuoka, LB Schwartz, SJ Galli, and WH Robinson |
March 2023
Molecular Mechanisms of Neurogenic Inflammation of
the Skin LM Jozefowicz, B Nedoszytko, M Grochocka, MA Zmijeweski, R Czajkowski, WJ Cubata & AT Slominski |
September 2019
Mast Cells and Sensory Nerves Contribute to Neurogenic Inflammation and Pruritus in Chronic Skin Inflammation
H Siiskonen & I Harvima |
|
June 2022
Neuroimmune communication regulating pruritus in atopic dermatitis M Steinhoff, F Ahmad, A Pandey, A Datsi, A AlHammadi, S Al-Khawaga, A Al-Malki, J Meng, M Alam & J Buddenkotte |
April 2018
Skin neurogenic inflammation JE Choi and A Di Nardo |
February 2018 Mast cell-neural interactions contribute to pain and itch K Gupta & IT Harvima |
|
November 2016
The Role of Neurotrophins in Inflammation and Allergy
S Manti, P Brown, MK Perez & G Piedimonte |
|